Cloud Basics
-
We'll use
- Nexus Artifact Repository
- Jenkins Build Automation
-
We don't install them locally but on servers.
-
IaaS: Infrastructure as a Service
- You can manage your own servers and infrastructure or
- Delegate infrastructure management
- Move your infrastructure to the cloud
- Just rent servers
- Using infrastructure which is set up and managed by someone else is IaaS
- Providers
- AWS
- GCP
- DigitalOcean
- Microsoft Azure
Setup Server on DigitalOcean
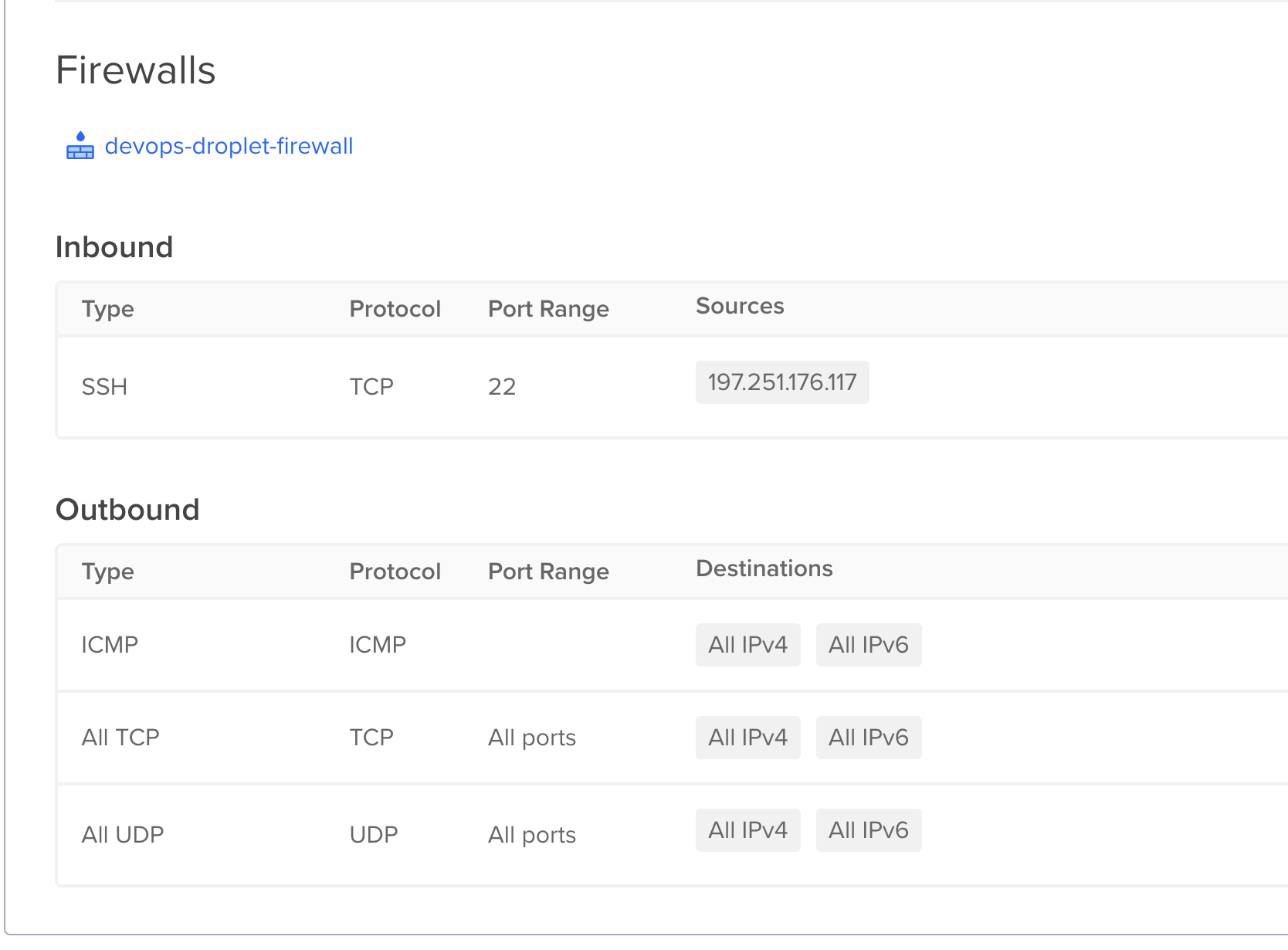
- By default, droplet has no firewall rules.
- Add port 22 for your current IP.
- Add droplet to firewall rule.
SSH into server
ssh -i .ssh/devops-droplet root@134.209.252.56
Install Java on Droplet
apt update
apt install openjdk-8-jre-headless
Deploy and run application artifact on Droplet
- Java app
- Build Jar file
- Copy to remote server
- Run app on the remote server
./gradlew build
- In build/libs, we want to copy to jar file to the server.
scp -i ~/.ssh/devops-droplet build/libs/java-react-example.jar root@134.209.252.56:/root
- After running the app, it starts on 7071. But port 7071 is not open by default
- Add inbound rule for port 7071
Run in detached mode
java -jar java-react-example.jar &
Checking running processes
ps aux | grep java
Use netstat to check running port
apt install net-tools
netstat -lpnt
Create and configure Linux user on the cloud server
- Best practice
- Create separate user for every application
- Give it only the permission it needs to run that app
- Don't work with the Root user
Add new user
adduser alfred
Add user to sudo group
usermod -aG sudo alfredasare
Switch user
su - alfredasare
$= Standard Linux User#= Root user
Print working directory
pwd
SSH for new users on server
- Ssh won't work for new user
- Switch to new user
- Create .ssh folder for new user
- Copy public key from local pc
- In ssh folder on server
sudo vim .ssh/authorized_keys
- Copy public key and save
- Can now ssh with this user
- We'll create a new user for every app we want to run on the server
- Don't start or run any apps with root
NB:
- If user need to run commands with sudo, you can add the user to the sudo group
usermod -aG sudo username